Abstract
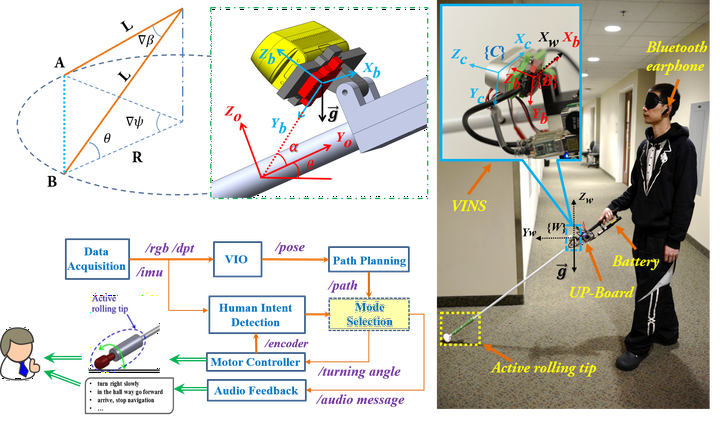
This paper introduces a new robotic navigation aid (RNA) for the visually impaired (VI). Two fundamental functions wayfinding and human-robot interaction (HRI) are presented for assisted wayfinding. The problem of wayfinding involves planning a path from the RNA’s current location to the destination and following the path to get to the destination. To address the problem, we developed a new visual inertial odometry to estimate the RNA’s pose by using the image and depth data from an RGB-D camera and the inertial data of an IMU. The estimated pose is used for path planning. To guide the user to follow the planned path, we designed an HRI interface with two guiding modes the robocane mode and white-came mode. In the robocane mode, the RNA uses a motorized rolling tip to steer itself into the desired direction of travel (DDT) for the user to follow and track the planned path. In the white-cane mode, the RNA uses its speech interface to indicate the DDT to the user by audio messages. In this mode, the user swings the RNA just like using a conventional white cane. To make mode selection effortless, we developed a human intent detection (HID) method based on the decision tree mode. The method can detect the user intent and automatically select the appropriate mode according to the detected intent. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacies of the VIO, HRI, and HID methods for assisted wayfinding.